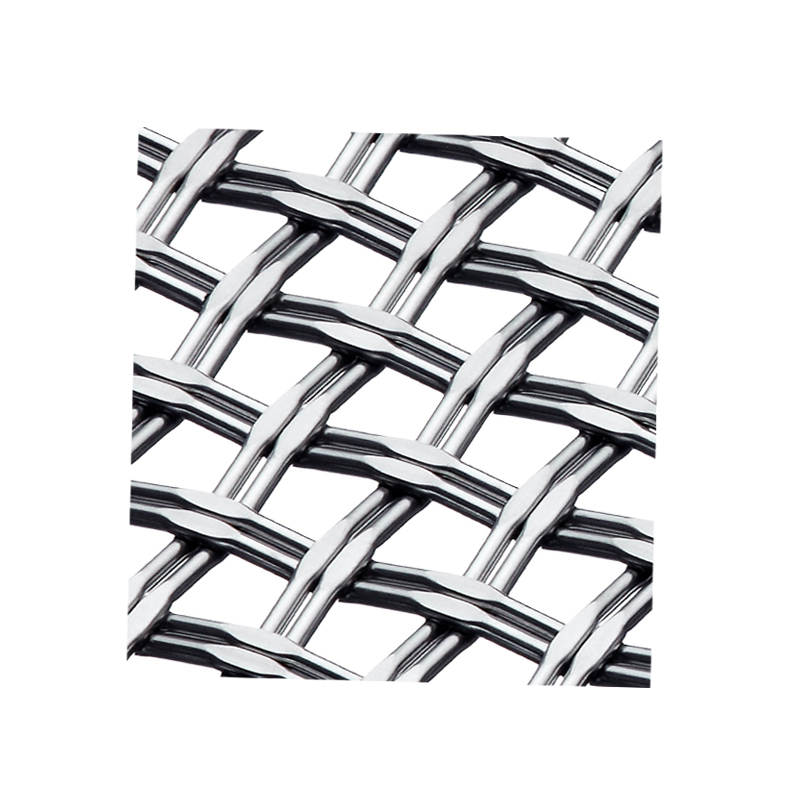
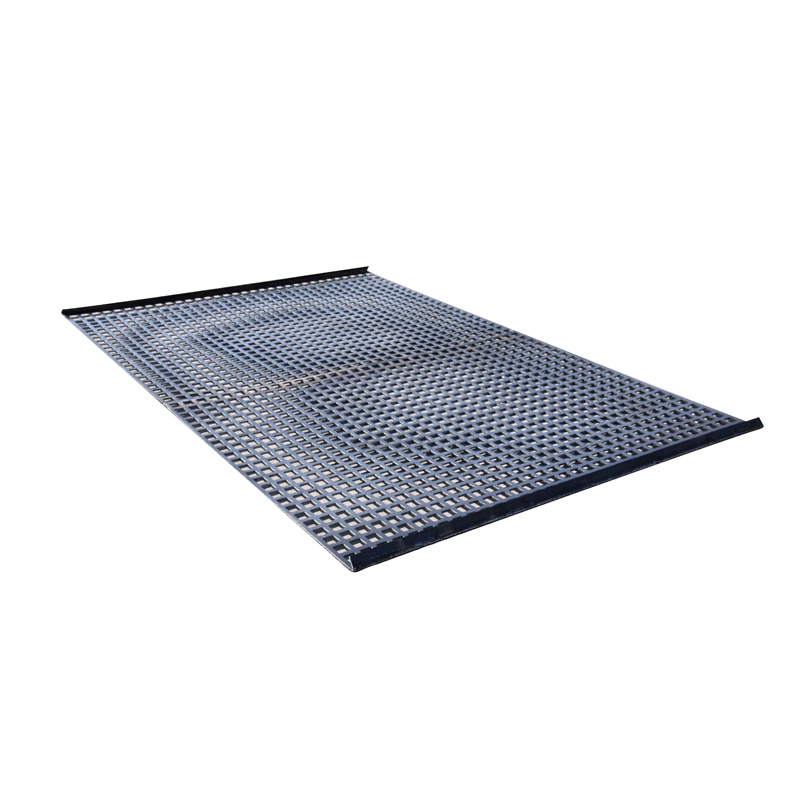
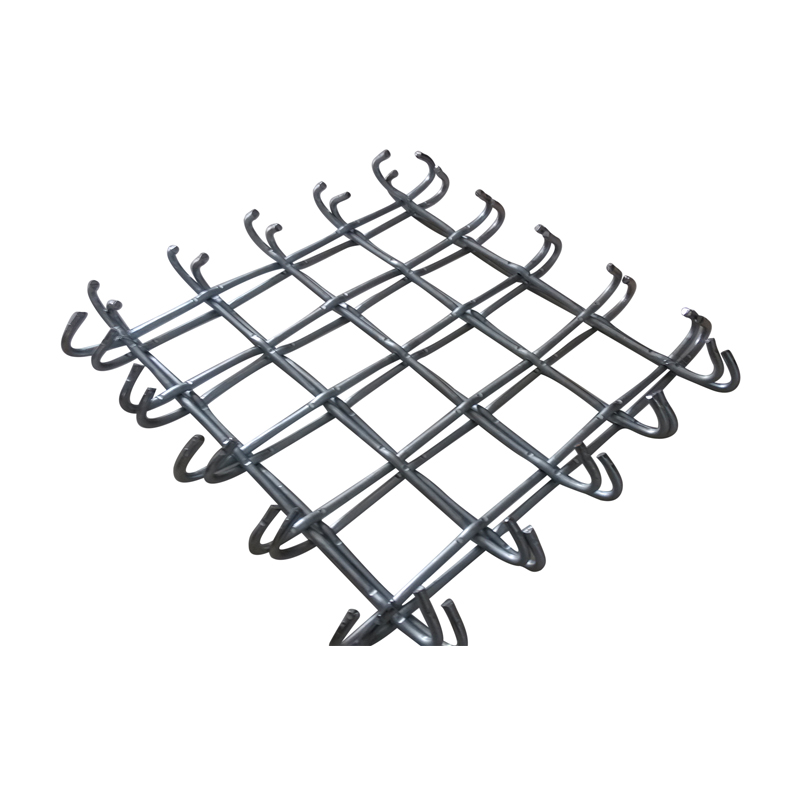
What is the difference between hot-dip galvanized welded wire mesh and cold-dip galvanized welded wire mesh?
Aug. 20, 2025
When new employees or buyers hear the terms hot-dip galvanized and cold-dip galvanized welded wire mesh, their first reaction is likely that hot-dip galvanizing is superior to cold-dip galvanizing. However, if you ask them in detail, "Why is hot-dip galvanizing superior to cold-dip galvanizing?" many of them might not be able to answer. Let me explain.
The hot-dip galvanizing process involves melting zinc and then immersing the cleaned welded wire mesh in the zinc bath. The high-temperature zinc molecules have a strong diffusion capacity, allowing them to bond well with the welded wire mesh. Furthermore, this coating provides a thicker zinc layer and better corrosion resistance. Expert testing has shown that hot-dip galvanized welded wire mesh remains intact after 100 hours in a salt spray environment, equivalent to 12 years of normal use. Let's analyze cold-dip galvanized welded wire mesh. Cold-dip galvanized welded wire mesh is produced by electrolyzing zinc at room temperature to produce a chemical reaction between the zinc and the welded wire mesh. Generally, cold-dip galvanizing results in a lower zinc content, so the welded wire mesh's corrosion resistance is inferior to that of hot-dip galvanizing.
Unlikely, most welded wire mesh is cold-dip galvanized. Hot-dip galvanizing is rare. Cold-dip galvanizing produces a more attractive surface than hot-dip galvanizing. However, hot-dip galvanizing is more practical. Furthermore, hot-dip galvanizing is performed in two different coating methods: 1. hot-dip galvanizing and 2. hot-dip galvanizing. As the name suggests, hot-dip galvanizing is performed under heated conditions. After the zinc is melted into liquid form, the base metal is immersed in it. This creates an interpenetrating bond between the zinc and the base metal, preventing impurities or defects from remaining between them. It's like the two materials have melted together at the coating. Furthermore, the coating is thick, reaching up to 100 microns, resulting in high corrosion resistance. It can withstand a 96-hour salt spray test, equivalent to 10 years under normal conditions. Cold-dip galvanizing, on the other hand, is performed at room temperature. While the coating thickness can be controlled, the bonding strength and thickness of the coating are relatively low, resulting in less corrosion resistance.
Hot-dip galvanizing is more expensive, while cold-dip galvanizing is cheaper. Cold-dip galvanizing also produces a brighter color.